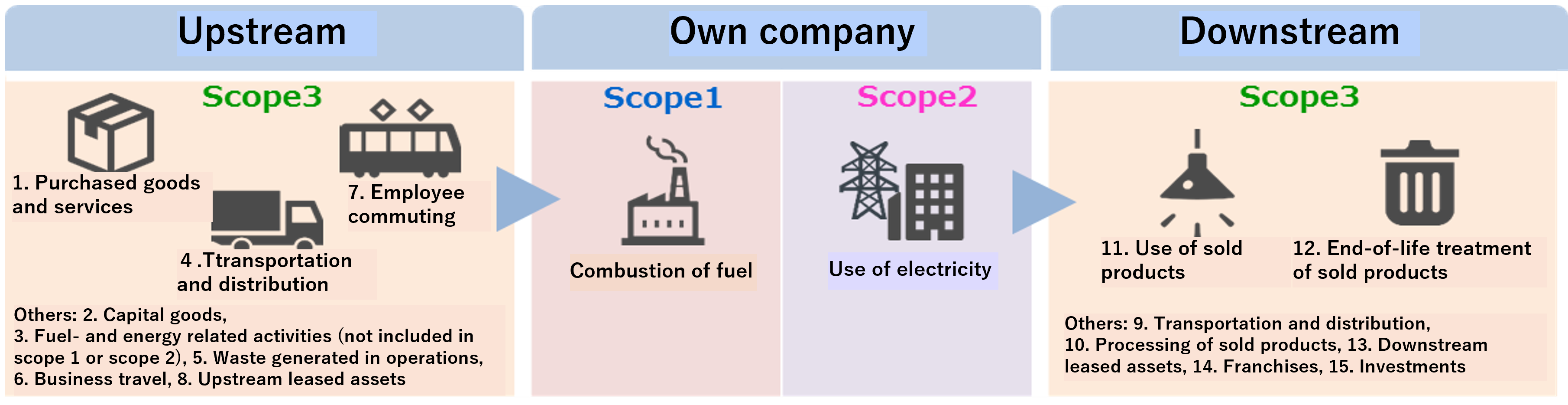
Roles of the OECC
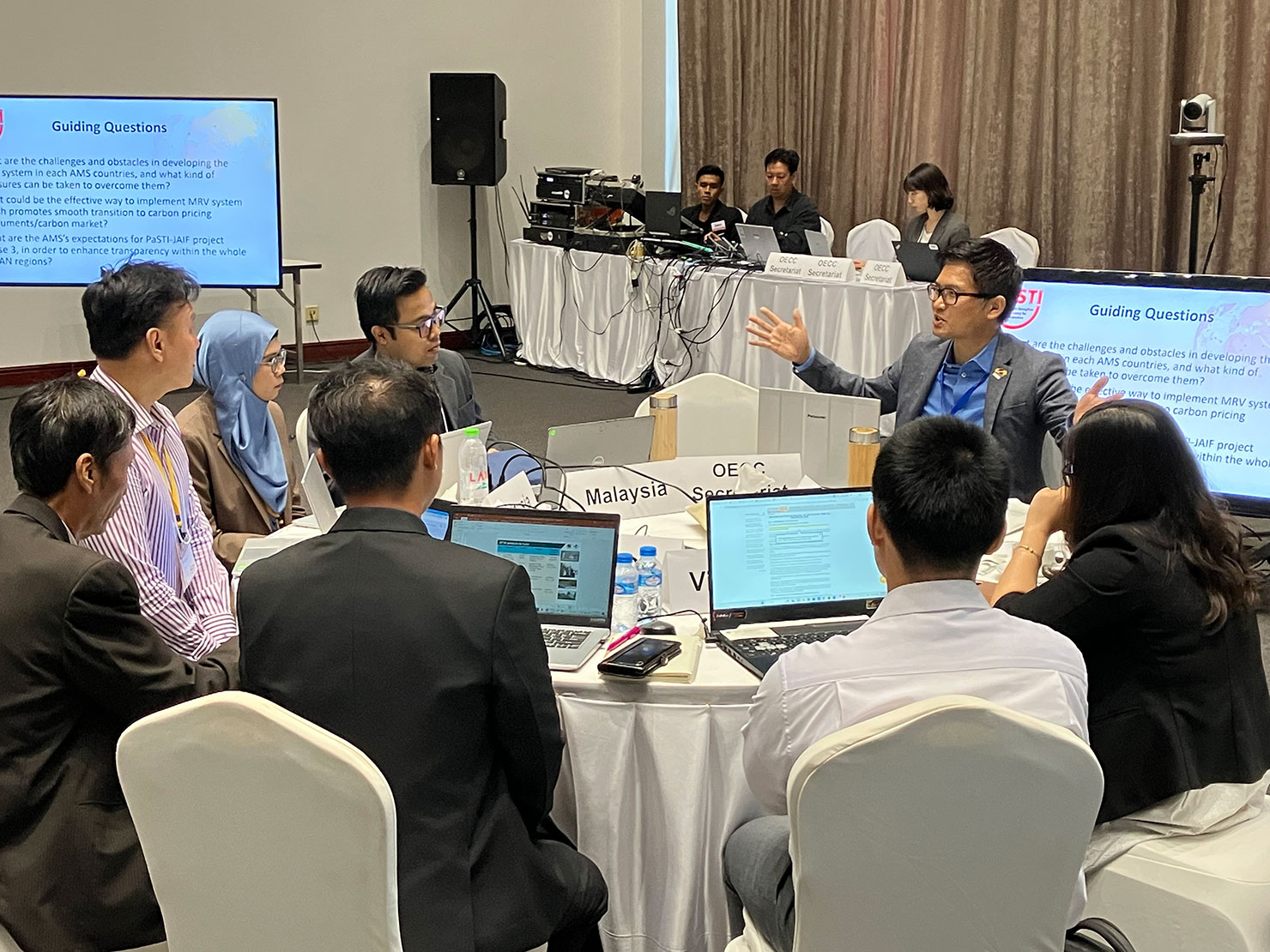
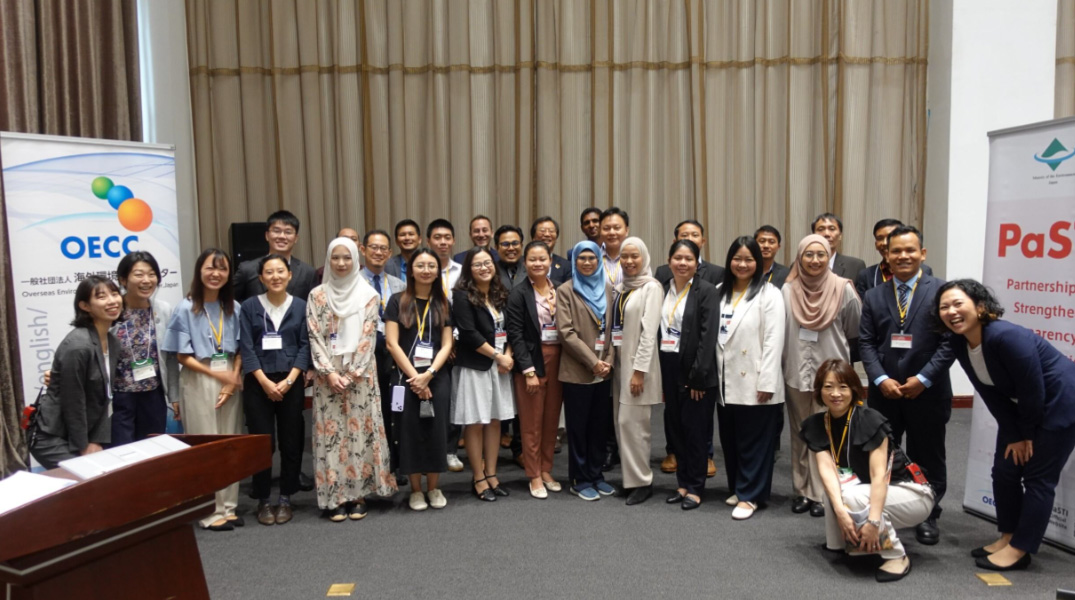
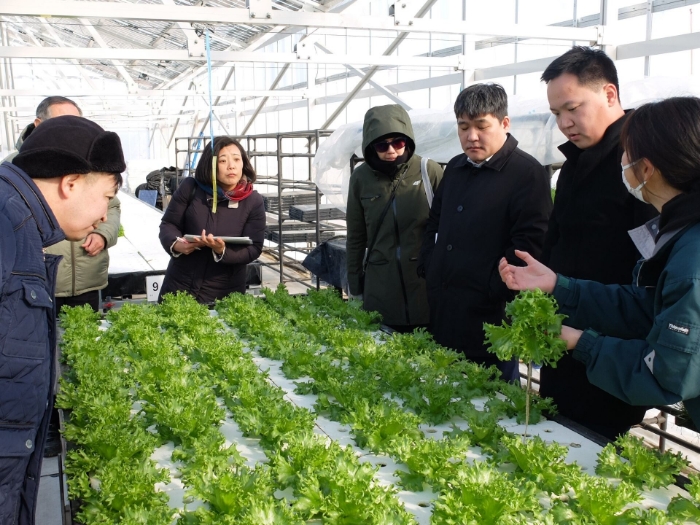
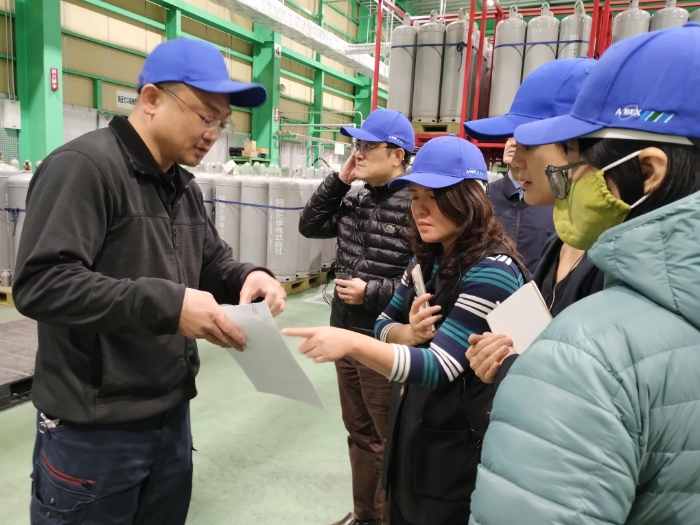
Under the Ministry of the Environment’s transparency initiative Partnerships to Strengthen Transparency for co-Innovation (PaSTI) and JICA’s technical cooperation projects, the OECC provides support in building and implementing systems related to calculating and reporting GHG emissions based on the needs of governments and companies in individual countries, including the development of laws and regulations. We also provide support through disseminating knowledge on the use of ESG finance as an incentive for companies to report their GHG emissions. In addition, we help Japanese companies strengthen their international competitiveness by supporting the visualization of GHG emissions in international supply chains.